Что такое гиалуроновая кислота с высоким молекулярным весом?
1гиалуроновая кислота и структурный состав
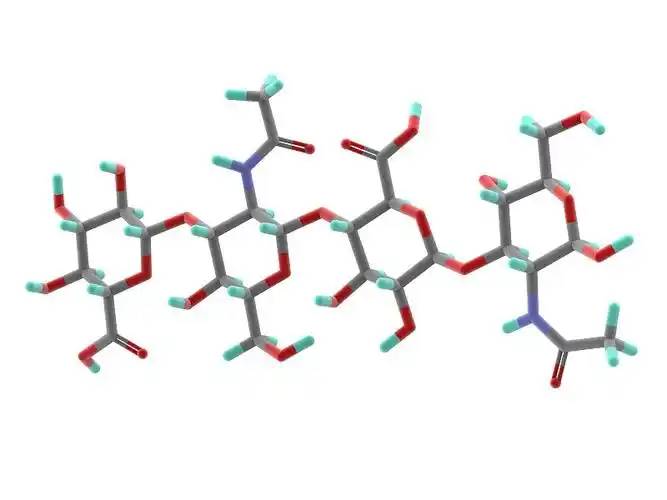
Hyaluronic - кислота;(HA) is a non-sulfated, high molecular weight linear polysaccharide with a basic structure consisting Соединенные Штаты америкиa disaccharide unit of D-glucuronic acid иN-acetylglucosamine, linked by a β- 1,3- ligand bond between В настоящее времяD-glucuronic acid and the N-acetylglucosamine, and by a β- 1,4- ligand bond between the disaccharide units (Figure 1). The molecular weight of natural - гиалуроническая болезньacid contained В случае необходимостиmost tissues ranges from 1000 to 10 000 kDa, and the definition of hyaluronic acid size has not yВ то же времяbeen fully agreed upon.According to Naro [1]1], high molecular weight hyaluronic acid is defined as consisting of more than 500 basic B. структурные измененияunits; intermediate molecular weights are generally in the range of 200-500 kDa, and small molecular weight hyaluronic acid is generally defined as less than 200 kDa. According to Monslow В то же времяal [2], high molecular weight (HMW hyaluronan) is >1000 kDa, medium molecular weight (MMW hyaluronan) is 250-1000 kDa, low molecular weight (LMW hyaluronan) is >10-250 kDa, and oligo hyaluronan (oligo hyaluronan) is <10 kDa.
The role of hyaluronan in cell motility, cell adhesion and proliferation is mainly mediated by two hyaluronan receptors, CD44 and R-hyaluronan MM (the receptor for hyaluronan-mediated motility, also called CD168). Unlike other mucopolysaccharides, which are synthesised in the Golgi apparatus, hyaluronan is synthesised in the inner membrane of the plasma membrane of the cell by transmembrane synthetases (hyaluronan S1, hyaluronan S2 and hyaluronan S3). Hyaluronan S1 and S2 are responsible for the synthesis of large molecules of hyaluronan and hyaluronan S3 is responsible for the synthesis of small molecules of hyaluronan (<300 kDa), but hyaluronan S3 is more active than hyaluronan S1 and hyaluronan S2 The synthesised large molecules of hyaluronan are cleaved В Том числе:small molecular weights of hyaluronan by ROS (reactive oxygen radicals) and hyaluronan hydrolytic enzyme, and further hydrolysed into low molecular weights of hyaluronan. Further hydrolysis results in oligo- or oligo-hyaluronic acid. Different molecular weights have different physiological functions, e.g. medium molecular weight hyaluronic acid stimulates cell proliferation, while small molecular weight hyaluronic acid promotes cell migration. See Table 1 [3- 19].
2 биологический прогресс гиалуроновой кислоты
2.1 гиалуроновая кислота и потеря веса
Hyaluronic acid has been approved as a new resource food in China (Ministry of Health Announcement No. 12, 2008), and is used as a food additive and food with health benefits in Korea, as a food additive in Japan, and as a supplement in the United States, Canada, Italy, and Belgium.
Breast milk contains the highest level of hyaluronic acid in the first week of life, which decreases to a stable level over the next two months. In general, a 70 kg adult has about 15 g of hyaluronic acid in his or her body, of which nearly one-third is degraded and synthesised on a daily basis. Hyaluronic acid is taken orally to the Кожа, цвет кожиand does not accumulate excessively in the body; more than 90% of hyaluronic acid is excreted in the breath or urine [19]. Hyaluronic acid is used for weight loss. When hyaluronic acid was administered to C57BL/6 mice at a dosage of 200 mg/kg for 8 weeks, it was found that hyaluronic acid had a good effect on weight loss, which not only reduced body mass, but also reduced adipose tissue and serum LDL-cholesterol, as well as total cholesterol and leptin, and also reduced adipose tissue hyperplasia, and ameliorated fatty liver. It is therefore hypothesised that the main mechanism of hyaluronic acid weight loss may be through the increase of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor PPAR-α and the inhibition of PPAR-γ [20].
2.2 гиалуроновая кислота и старение
Hyaluronic acid and hyaluronan-binding proteins are involved in cellular senescence. Researchers have found that hyaluronic acid can heal skin damage caused by UV-B exposure through histological changes and wrinkle indicators in vivo. Moreover, high concentrations of hyaluronic acid significantly affected the expression of collagen, matrix metalloproteinase (MMP-1), interleukin IL-1β and interleukin IL-6 protein factors, but not hyaluronan S-2 and transforming growth factor (TGF-β1). Reduction of proteoglycans leads to an increase in free hyaluronan fragments interacting with CD44 protein and phosphorylation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase ERK1/2, resulting in premature embryonic fibroblast failure [21].

Inhibition of hyaluronan synthesis by 4-methylumbelliferone or targeting of hyaluronan S-2 by miRNA induces cellular senescence, suggesting that hyaluronan plays a role in skin ageing [22]. Кроме того, hyaluronan concentration is greatly reduced in senescent MSCs and in the cell cycle matrix, mainly due to reduced expression of hyaluronidase [23]. Considering the ability of hyaluronan to inhibit fibroblast senescence induced by oxidative stress in vitro [24]. Thus, hyaluronic acid may be involved in ageing during normal and pathological processes. Further investigation of the role of hyaluronic acid in aging in disease states may shed light on the pathogenesis and aid in the development of therapeutic approaches for these diseases.
2.3 гиалуроновая кислота и рост и развитие
Hyaluronan participates in and promotes cell growth through a variety of signalling pathways. In mice in which the hyaluronan gene hyaluronan s2 was knocked out, the heart and blood vessels developed abnormally, and at 9.5 weeks of development, the lack of an intact endocardial cushion resulted in embryonic lethality (TD Camenisch, 2000). Intraperitoneal injections of hyaluronic acid for 3-8 weeks increased the length of villi and depth of the glandular fossa in the small intestine, the depth of the glandular fossa in the colon, and the proliferation of epithelial cells in both. The opposite results were obtained with PEP-1, a short peptide that prevents the binding of hyaluronan to the receptor. These results suggest that endogenous hyaluronan can regulate normal small bowel and colon growth.
Hyaluronic acid and its binding proteins have been shown to play a role in fibroblast proliferation. Hyaluronic acid promotes TGF-β1-mediated fibroblast proliferation, and LMW hyaluronic acid or hyaluronan - олигосахаридыstimulate fibroblast proliferation under a variety of conditions, suggesting that hyaluronic acid plays an important role in tissue fibrosis. Hyaluronic acid fragments induced myofibroblast differentiation, endothelial cell differentiation, and chondrogenic differentiation [25], whereas hyaluronic acid and mouse tumour necrosis factor α-inducible protein 6 inhibited cardiomyocyte differentiation and osteoclast differentiation of По правам человекаbone marrow mesenchymal stem cells, respectively. These data suggest that hyaluronan and hyaluronan-binding proteins regulate cell differentiation in a complex manner and that this differentiation may be related to cell type and microenvironment.
2.4 гиалуроновая кислота и иммуновоспаление
Hyaluronic acid and hyaluronan-binding proteins regulate inflammation and the repair of tissue damage by modulating the infiltration of inflammatory cells, the release of inflammatory cytokines and cell migration. Therefore, hyaluronic acid may act as an immunomodulator in human diseases [26]. Synthetic hyaluronic acid has been found to promote the expression of antimicrobial peptides in intestinal epithelial cells. Oral administration of hyaluronic acid from breast milk induced an increase in mouse defensin HβD2 homologue and MuβD3 via Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and CD44 protein, and the addition of hyaluronic acid cytokines to cultured cells showed that colonic mucosal epithelial cells were more resistant to the enteropathogenic bacterium Salmonella typhimurium. Hyaluronic acid regulates cell proliferation and inflammation.
Воспалительные клетки активируют кератиноциты для получения interleukin IL- 6, IL-1 и опухолевого фактора некроза (TNF- α) путем высвобождения цитокинов и образования фрагментов гиалуронана LMW, что, в свою очередь, увеличивает синтез гиалуронана частично за счет действия гб-egf, а обратная связь гиалуронана способствует воспалительным реакциям, включая миграцию и распространение фибровзрыва. Гиалуроновая кислота сообщается RMA В то же время- эл. - привет.С. гиалуронан рма и др. [25] сообщили, что гиалуроническая кислота в сочетании с куркумином способствует распространению кератиноцитов, снижает окислительные повреждения, вызываемые перекидом водорода, и улучшает миграцию клеток в местах царапин.
Hyaluronic acid can be utilised by probiotics. Probiotics can use N-acetyl-D glucosamine, a precursor of hyaluronic acid, as a nutrient, and Kim В то же времяal [27] found that Lactobacillus plantarum K8 lysate significantly increased hyaluronic acid secretion from cells. Lactobacillus lysates inhibited the Th2 response induced by interleukin 4 (IL-4)-driven stimulation and increased the Th1 response, and lactobacilli controlling the Th1/Th2 balance contributed to hyaluronic acid induction and the reduction of atopic dermatitis lesions.
Hyaluronic acid and CD44 interact with each other and have the ability to modulate T-cell activation, Th1 production, B-cell activation and regulatory T-cell functions. Recent studies have shown that CD44 functions in the adaptation of regulatory T cells by interacting with galactose agglutinin 9 [28].
Hyaluronic acid and CD44 regulate neutrophil adhesion and recruitment. It is endothelial CD44, not neutrophil CD44, that mediates neutrophil migration, and hyaluronic acid is also capable of promoting the production of inflammatory vesicles in response to injury. In CD44-/- deficient mice, lymphocytes preferentially stayed in lymph nodes and delayed their entry into synovial joints with an inflammatory response compared to wild-type cells. CD44-/- deficient mice die from non-infectious pneumonia injury, a continuous inflammatory response characterised by impaired clearance of apoptotic neutrophils [26]. In addition, hyaluronan fragments can affect dendritic cell maturation, e.g. LWM hyaluronan fragments not only induce dendritic cell maturation but also switch on alloimmunity. In addition, hyaluronan - олигосахаридыare potential activators of dendritic cells, allowing small molecule hyaluronan fragments to promote cell migration and subsequent allergic modifications.
Кроме того, TLR-4, природный рецептор липополисахарида, является одним из гиалуронанских рецепторов. TLR-4 активирует ядерный коэффициент транскрипции NF- kB протеин двумя путями: Один вызывает провоспалительные цитокины через зависящий от миелоида фактор дифференциации миелоида MyD88, а другой — не зависящий от миелоида путь MyD88, который увеличивает вызываемые интерфероном провоспалительные гены с помощью интерферонов типа I [26].
2.5 гиалуроновая кислота и Рак
Hyaluronic acid not only acts as a cellular support and hydrophilic matrix, but also regulates cell adhesion, migration, growth and differentiation (TC Laurent, 1992). These properties have led to the involvement of hyaluronic acid in a number of pathological processes. For example, in cancer, hyaluronic acid forms a protective film on the surface of tumour cells, making them less vulnerable to attack by immune cells. At the same time, tumour cells produce more hyaluronic acid or induce the production of hyaluronic acid by releasing growth factors and cytokines. Moreover, ROS-induced hyaluronan fragments contribute to the efficient expression of hyaluronan (R Stern, 2006). Tumour cells and stromal cells are able to express hyaluronan homologues and produce hyaluronan-containing extracellular matrix, which accumulates in the tumour and pericancerous stromal tissues, thus accelerating metastasis of cancer cells [29].
In addition, hyaluronic acid also regulates fibroblast and tumour invasion (Q Yu, 2000). Transforming growth factor and tyrosine kinase, when activated, regulate hyaluronan-mediated invasive cellular motility [27]. Heterogeneity analysis of probe cells using hyaluronan resulted in the identification of subtypes of infiltrating but slow-growing breast tumours. By analysing Фибробласты и фибробластыisolated from transgenic mice overexpressing hyaluronan S2, we found that the cells had a greater ability to invade the stroma. If the hyaluronan S2 gene is knocked out of mesenchymal cells, the invasive fibroblast phenotype is terminated, the accumulation of myofibroblasts is discharged and the development of lung fibrosis is inhibited [30].
2.6 корреляция гиалуроновой кислоты со стволовыми клетками
The interaction of hyaluronic acid with stem cells has been studied in haematopoietic stem cells, MSCs and pluripotent adult progenitors, suggesting that hyaluronic acid and its binding proteins may interact with various stem cells through their ability to regulate tissue damage and repair processes. During stem cell differentiation, hyaluronan synthesis was enhanced 13-fold and 24-fold, most likely due to an increase in hyaluronan S2 expression. Hyaluronan is required for the production of haematopoietic cells during human embryonic stem cell differentiation. Knockdown of hyaluronan S2 resulted in inhibition of human embryonic stem cell differentiation. Hyaluronan oligosaccharides increase the stem cell properties of epi- кожные покровыcells by regulating integrins. Hyaluronic acid promotes CD44-dependent migration of MSCs CD44 has long been used as a marker for stem cells, including embryonic, mesenchymal, haematopoietic and cancer stem cells. In addition, CD44 may play a role in regulating stem cell function. A recent study has shown that although CD44 is not a master stem cell gene, CD44 contributes to stem cell generation and the homeostasis of stem cells in their ecosystem. Hyaluronic acid is required to regulate the haematopoietic support function of bone marrow helper cells and is involved in haematopoietic site assembly.
2.7 гиалуронан и апоптоз
In bleomycin-induced lung injury, hyaluronic acid protects mouse lung epithelial cells from apoptosis. High molecular weight hyaluronic acid reduces UV-induced apoptosis and inflammation in human epithelial corneal cells. Dermal fibroblasts are resistant to stress-induced apoptosis in the presence of high levels of hyaluronan s2 gene expression in the presence of hyaluronan s1/3 knockout, suggesting that hyaluronan S2 protects dermal fibroblasts from environmental stress-induced apoptosis. For inflammatory cells, hyaluronic acid appears to induce apoptosis. Hyaluronic acid appears to induce apoptosis. Hyaluronic acid induces apoptosis in activated T cells via CD44. LMW hyaluronic acid-TLR4 interaction induces apoptosis in inflammatory neutrophils. In rats, administration of hyaluronic acid with a molecular weight of 1600 kDa significantly reduced smoke-induced neutrophil infiltration, pulmonary oedema, respiratory apoptosis and mucus plugging, suggesting that high-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid may have a potential therapeutic effect on smoking-induced lung injury. In addition, cross-linking of CD44 molecule-specific epitopes rapidly induced neutrophil apoptosis in vitro and inhibited neutrophil-dependent renal injury in rats in vivo.
2.8 роль в миграции клеток и вторжении в них
Hyaluronic acid mediates inflammatory cell migration to regulate the inflammatory response and tissue damage.CD44 deficiency leads to increased neutrophil migration and lung injury in E. coli pneumonia in mice. TSG6 is a potent inhibitor of neutrophil migration in an in vivo model of acute inflammation. Exogenous Гиалуроновая кислота с низким молекулярным весом, or LWM hyaluronic acid produced by overexpression of HYAL1, promotes the migration of dendritic cells from the skin and subsequently alters the allergic response in a TLR4-dependent manner. Hyaluronan and hyaluronan-binding proteins play a role in fibroblast migration and smooth muscle cell migration. Abnormal accumulation of hyaluronan matrix promotes fibroblast migration.
Specifically sized hyaluronan oligosaccharides stimulate fibroblast migration and excisional wound repair. both CD44 and HMMR have been shown to have a role in fibroblast migration during tissue injury. In addition, myofibroblast migration can be regulated by hyaluronic acid. These studies suggest a role for hyaluronic acid in tissue injury and fibrosis. Small molecular weight hyaluronic acid35 and high molecular weight hyaluronic acid117 showed significant differences in the migration and invasion of breast cancer 4T-1 and SKBR3 cells. In healthy people, the level of hyaluronic acid in the body is 10-100 μg/- L,but in breast cancer patients, the level is as high as 200-300 μg/L, and in advanced breast cancer, it reaches 789-2343 μg/L (EH Cooper, 1988). Compared with small molecular weight hyaluronic acid, high molecular weight hyaluronic acid is able to exert a greater squeezing force on the tumour spheres and prevent the growth of cancer cells. Small molecular weight hyaluronic acid can accelerate the process of metastatic fibrosarcoma cell invasion [9].
3 перспективы на будущее
Over the past decades, hyaluronic acid and its hyaluronan receptor have been intensively investigated, leading to an increasing use of hyaluronic acid. Nevertheless, there are still some problems that need to be solved. The first problem to be solved is the definition of high molecular weight and low molecular weight hyaluronic acid. There is no international consensus on the distinction between high and low molecular weight hyaluronic acid, which poses a problem in elucidating the physiological effects of hyaluronic acid on cells. Secondly, high molecular weight hyaluronic acid controls the normal homeostasis of the body and shows anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer effects, while low molecular weight hyaluronic acid and oligo-hyaluronic acid show pro-inflammatory and pro-cancer effects. If the same receptor is used, but the results are significantly different, the mechanism is still not clear. In addition, how hyaluronic acid precisely regulates the occurrence and development of inflammation and tumour cells; whether oral administration of hyaluronic acid affects the intestinal flora, which in turn affects human health; and how modified hyaluronic acid (e.g., sulphated hyaluronic acid) has a different mechanism of action compared with non-modified hyaluronic acid, need to be further elucidated. The solution of these problems will certainly help to prevent diseases and maximise the use of hyaluronic acid for the treatment of human diseases.
Ссылка на сайт
[ 1] нет д. Редакционная работа: взаимодействие между hyaluronic acid and Его рецепторы (CD44, RHAMM) регулирует деятельность воспаления и рака [J]. Передняя иммунола, 2016,7:39.
[2] монслоу дж., говиндараджу П, чистый е. Гиалуронан-а Функциональные и функциональные structural - с удовольствием. Пятно в микросреде ткани [J. []. Передняя иммунизация, 2015,6 :231.
[3]Karbownik M- с,новак JZ. Гиалуронан: к новым анти-терапии рака [J]. Фармакол Rep, 2013,65(5):1056- 1074.
[4]Papakonstantinou E, Roth - м,Karakiulakis G. гиалуроновая кислота: ключевая молекула в старении кожи [J]. Дерматоэндокринол, 2012,4(3): 253 — 258.
[5]Kavasi R- м,Berdiaki A, Спиридаки I, И др. Ха метаболизм в гомеостазе кожи и воспалительных заболеваниях [J]. Food Chem Toxicol, 2017,101:128- 138.
[6] чжу и, ху дж., ю т., и др. Гиалуроновая кислота с высоким молекулярным весом подавляет фиброз эндометрия [J]. Организация < < мед > > Sci Monit, 2016,22: 3438 — 3445.
[7] чжао иф, цяо сп, ши сл и др. Модуляция трехмерной микросреды гиалуронаном различных молекулярных весов изменяет поведение клеток рака молочной железы [J]. Оао апл - добрый день. Интерфейсы. 2017,9(11):9327 — 9338.
[8]Благородство и слава богуНу и ну.Lake FR, Henson PM и др. Гиалуронат активация CD44 вызывает инсулин-как фактор роста - 1 выражение с помощью фактора некроза опухоли-альфа-зависимого Объединенных наций в области Муринемакрофаги [J]. J Clin Invest, 1993,91(6):2368- 2377.
[9] ходж — Dufour - джей, Noble PW, - хортон. - мистер, et - эл. - привет. 3. Вводный курс Из иль - 12 и хемокинов гиалуронан требует адгезии-зависимого привода резидента, но не возбужденных макрофагов [J]. J иммунол, 1997, 159 (5): 2492- 2500.
[10]Ohkawara Y, Tamura G, Iwasaki T, и др. Активация и преобразование - Ing фактор роста-бета-производство в эозинофилах hyaluronan[J]. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol, 2000,23(4):444 — 451.
[11]Fitzgerald KA, Bowie AG, Skeffington BS и др. Ras, белковый киназ C zeta, и I kappa B kinases 1 и 2 являются следующими эффектами CD44 во время активации NF- kappa Bby hyaluronic acid фрагментов T- 24 раковых клеток [J]. Jиммунол, 2000,164(4):2053 — 2063.
[12] слевин M, 3. Кумар S, - гаффни. - джей. - привет. - ангиоген. oligosaccharides Гиалуронаны вызывают многочисленные сигналы, влияющие на сосудистые системы Митогенные реакции эндотелиальных клеток и заживление ран [J]. J биол (биол) Химия, 2002,277(43): 41046- 41059.
[13]West DC, Kumar S. Hyaluronan and angiogenesis [J]. Ciba Found Symp, 1989,143: 187- 201; Обсуждение 201- 187 281- 185.
[14] западный округ Колумбия, кумар с. эффект гиалуроната и его олигосахача - Скачки по распространению эндотелиальных клеток и целостности моноляров [J]. Exp Cell Res, 1989,183(1):179- 196.
[15] вистейнова L, - сафранкова. - B, Новости компании "неспорова" - к, et - эл. - привет. Гиалуронан с низким молекулярным весом опосредованный CD44 зависимая индукция IL- 6 и Хемокины (химическая химия) in human dermal fibroblasts 2. Потенциальные возможности Врожденная иммунная реакция [J]. Цитокин, 2014, 70(2):97 — 103.
[16] термер CC, c, c - хенни. - привет. - джей, - фойт. - с, et - эл. - привет. - олигосахариды Гиалуронан-мощные активаторы дендритных клеток [J]. J иммунол, 2000,165(4):1863- 1870.
[17]Pandey MS, Багенстос ба, уошберн джей и др. Гиалуронанский рецептор для эндоцитоза (HARE) активирует NF- kappaB- опосредованное выражение гена в ответ на 40- 400- кда, но не меньше или больше, гиалуроны [J]. J Biol Chem, 2013, 288(20):14068 — 14079.
[18] гатак с, мисра с, тул бп. Гиалуронан олигосахариды ингибитное крепление-самостоятельный рост опухолевых клеток путем подавления фосфоинозида 3- киназа/акт пути выживания клеток [J]. J Biol Chem, 2002, 277(41): 38013- 38020.
[19]Oe M, Mitsugi K, Odanaka W, et al. Диетическая гиалуроновая кислота мигрирует into the skin of Крысы [J]. По научным исследованиям В мире Дневник,2014,2014:378024.
[20]Park BG, Park YS, Park JW и др. Анти-потенциал ожирения энзиматических фрагментов гиалуронана на высоком-жировая диета-индуцированное ожирение у мышей C57BL/6 [J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2016,473(1): 290 — 295.
[21] суван к, чучип к, хатано с и др. Versican/PG- M соединяет гиалуроны во внеклеточную матрицу и ингибирует CD44- медитированный сигнал к преждевременному старению эмбриональных фибробластов [J]. J Biol Chem, 2009,284(13): 8596 — 8604.
[22] ломпардия - SL, - пападеметрио - ди-эл, Тушь для ресниц M, et al. Лейкемические клеточные линии человека синтезируют гиалуроны, чтобы избежать старения и противостоять химиотерапии [J]. Гликобиология, 2013,23(12):1463 — 1476.
[23] юнг ем, квон о, квон кс и др. Доказательства корреляции должны быть - Подростковый сокращенный VCAM- 1 экспрессия и гиалуронанный синтез при клеточном старении мезенхимальных стволовых клеток человека [J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2011,404(1): 463 — 469.
[24]Cirillo N, Vicidomini А, маккаллоу м, и Эл. На основе гиалуроновой кислоты Соединение ингибирует фибробласт Старение, вызванное окислительным стрессом in vitro и предотвращает пероральный мукозит in vivo[J]. J телосложение клеток, 2015,230(7): 1421 — 1429.
[25] шарма м, саху к, сингх сп и др. Лечение ран деятельность cur- Тмин в сочетании с гиалуроновой кислотой: in vitro и in vivo evaluation [J]. Artif клетки наномед биотехнол, 2017,28:1- 9.
[26]Jiang D, Liang J, Noble PW. Гиалуронан как иммунный регулятор при заболеваниях человека [J]. Physiol Rev, 2011,91(1):221 — 264.
[27] ким х, ким р, чон бж, И др. Влияние орального приема лисатов kim- chi- производных Lactobacillus plantarum K8 на увлажнение кожи-ing. J Microb hyaluronic подкисление биотехно [J], 2015,25(1):74 — 80.
[28]Wu C, Thalhamer T, Franca RF и др. Взаимодействие Galectin- 9- CD44 повышает стабильность и функциональность адаптивных регулятивных T-клеток [J]. Иммунитет, 2014, 41(2):270 — 282.
[29] хельдин P, басу к, олофссон б и др. Дерегулирование синтеза, деградации и связывания гиалуронанов способствует развитию рака молочной железы [J]. J Biochem, 2013,154(5): 395 — 408.
[30]Li Y, Jiang D, Liang J, et al. Тяжелый фиброз легких требует инва - Сивный фибробластный фенотип, регулируемый hyaluronan и CD44[J]. J Exp Med, 2011, 208(7):1459 — 1471.


 Английский язык
Английский язык Французский язык
Французский язык На испанском языке
На испанском языке Русский язык
Русский язык Корейская народно-демократическая республика
Корейская народно-демократическая республика На японском языке
На японском языке